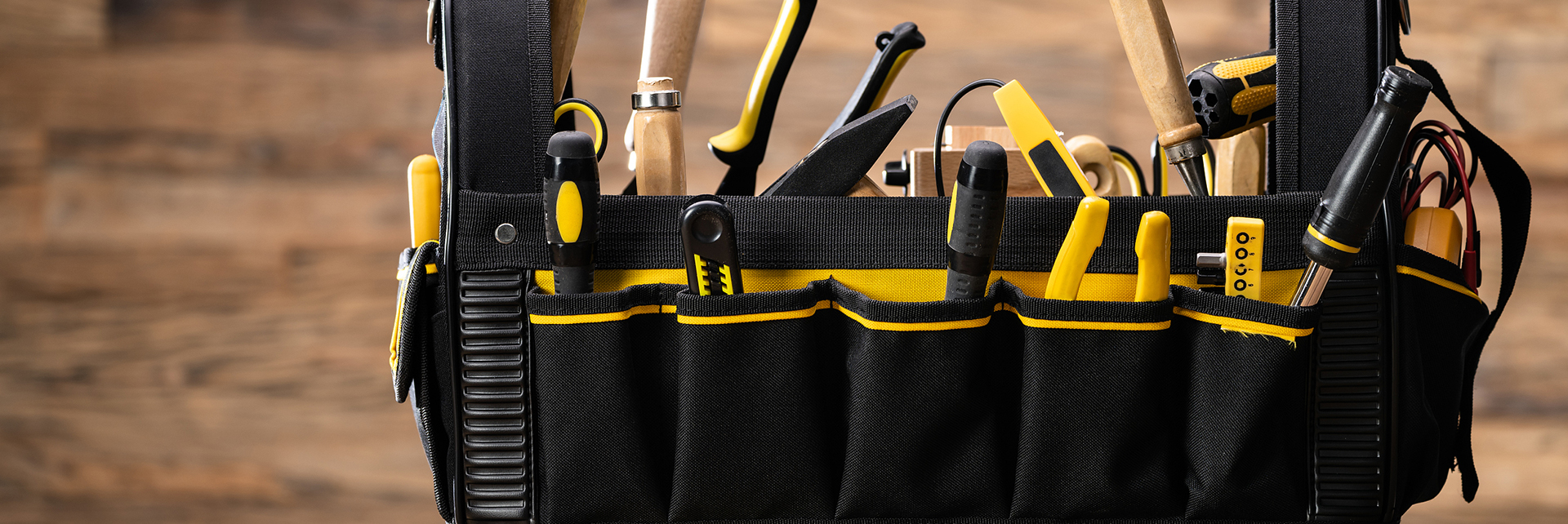
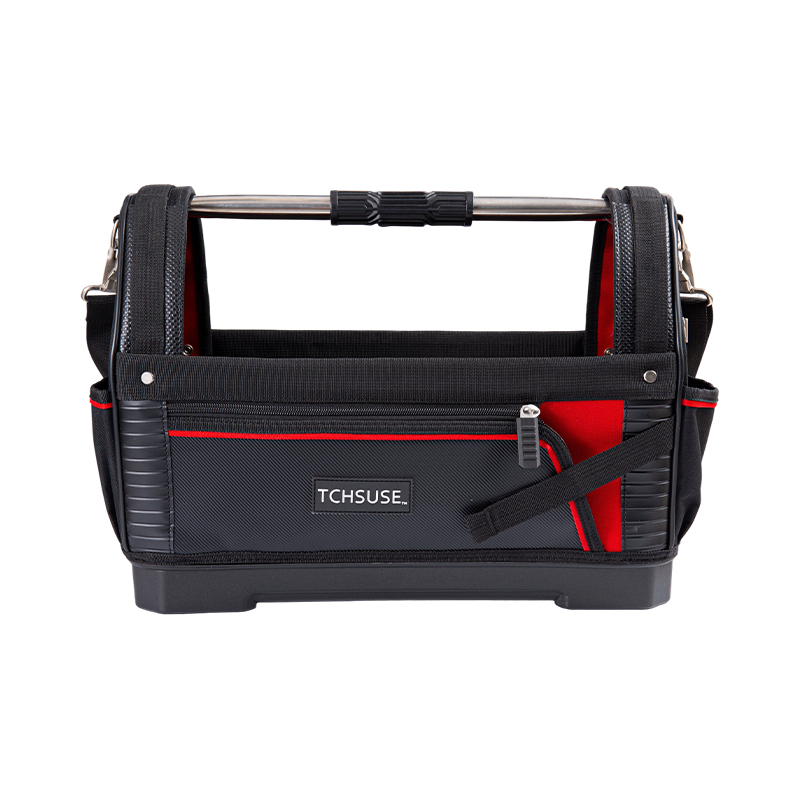
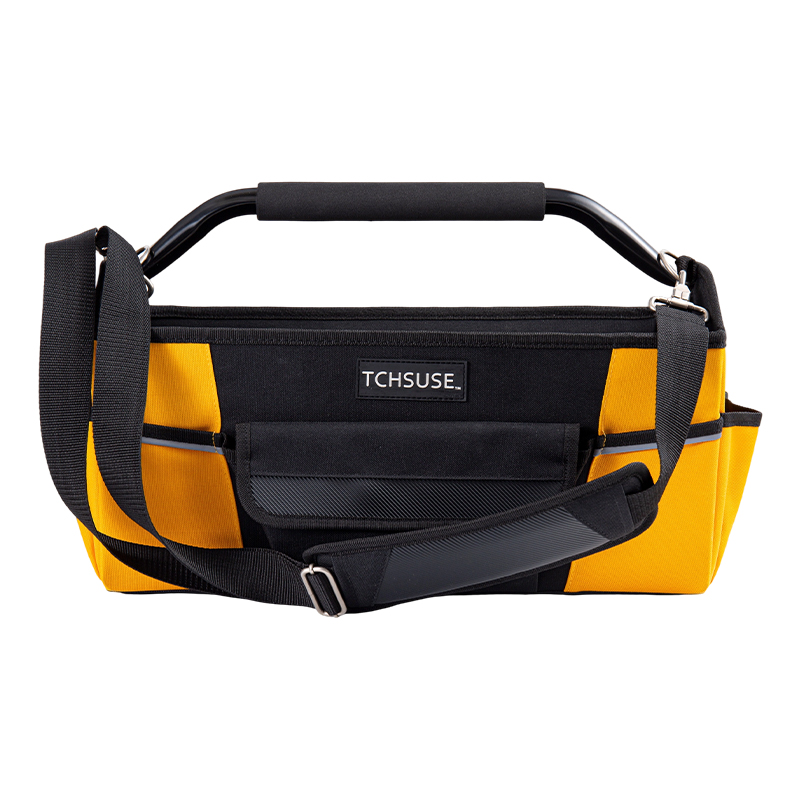
How Does the Partition Design of a Tool Belt Bag Optimize Tool Storage Efficiency?
The partition design of a tool belt bag is a key factor in improving work efficiency, directly impacting a worker's ability to quickly find the tools they need on-site.
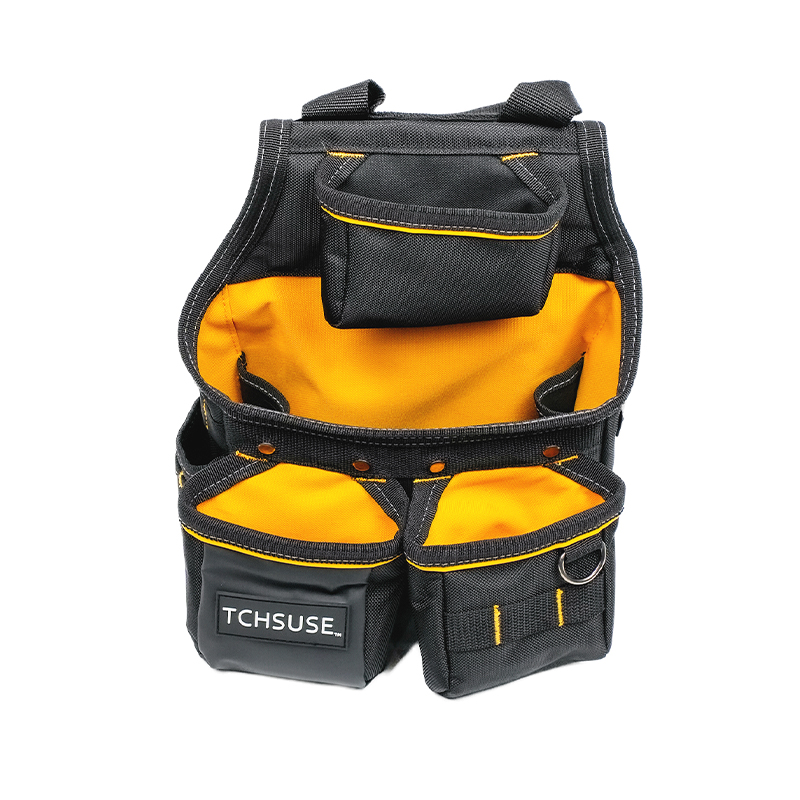
Number of Partitions and Pocket Layout
- Multiple Pocket Layout allows for categorization by tool type (screwdrivers, pliers, measuring tapes, voltage testers, nail guns), reducing search time.
- Combination of Large and Small Pockets: Large pockets are used to store large tools (such as wrenches and handsaws), while small pockets are used to store small tools such as screws, pencils, and electric screwdriver bits.
- Hierarchical Partitioning: Vertical or horizontal dividers inside the belt bag prevent tools from being stacked haphazardly and make them easily visible when needed.
Hanging Rings, Hooks, and External Fixing Points
- Hanging Ring/D-Loop Design allows for hanging measuring tapes, hammers, or multi-tools, freeing up internal pocket space and keeping tools organized.
- Adjustable hooks allow users to freely adjust their position according to tool length or usage frequency, improving retrieval efficiency.
Ease of Access and Quick Operation
- Frequently used tools should be placed in the front of the waist or an easily accessible pocket, ensuring quick one-handed access.
- Different tool types should consider the angle and direction of access: sharp tools should be placed vertically to prevent accidental injury, small tools should be laid flat or have elastic pockets to prevent them from falling.
Material and Elastic Design for Effective Partitioning
- Elastic mesh pockets or stretchable pockets can accommodate tools of different sizes and prevent movement.
- Reinforced dividers maintain shape stability and prevent tools from being squeezed and deformed.
Does the Tool Belt Bag consider symmetry and ease of use for left- and right-handed users
Ergonomics requires that tool belt bags be as universally compatible as possible for both left- and right-handed users, while ensuring ease of use and safety. A well-designed symmetrical layout and modular design not only improve efficiency but also reduce work fatigue.
Symmetrical Design Principles
- Side pockets, loops, and compartments should be symmetrical to allow for convenient operation by both left- and right-handed users.
- Adjustable belts and rotating hooks ensure stability when the belt bag is worn at different waist heights and on the left/right side.
- Frequently used tools (such as measuring tapes, screwdrivers, and voltage testers) should be placed on the side of the user's hand for quick one-handed access, while avoiding fatigue or injury caused by excessive reaching or twisting of the waist.
Modular and Adjustable Design
- Detachable pouches or rotating hooks allow for free switching between left- and right-handed use, catering to different user habits.
- Modular design allows for easy layout adjustments based on tool type and usage scenario (electrician, plumber, carpenter, DIY), improving tool storage flexibility and security.
Enterprise Technological Advantages—Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd.
- Functional Design: The company designs functional zones based on different tool types and usage scenarios (e.g., plumbing, carpentry, home DIY), ensuring convenient operation for both left- and right-handed users.
- Collaborative Development: Combining customer design sketches with the company's engineering optimization solutions, ergonomic, high-quality waist packs are developed, directly suitable for mass production.
- Global Applicability: Products meet European, American, and Asian market standards, including ISO certification and RoHS environmental requirements, ensuring safe and convenient use for users in different regions.
- Precision Tool Storage Solutions: Customized storage solutions are provided for precision instrument brands, ensuring small tools or precision parts remain stable and easily accessible for both left- and right-handed users.
Safety and Comfort Considerations
- Symmetrical and modular design reduces user twisting or reaching movements, lowering shoulder and back strain.
- Flexible hanging and pocket layout prevents tools from falling when working at heights or on the move, improving on-site safety.
What are the differences in design requirements for Tool Belt Bags among different professions (electrician, carpenter, plumber, construction worker)?
Different professions have significantly different functional and design requirements for tool waist bags, mainly reflected in the type of tools, capacity, durability, and safety:
|
Profession
|
Tool Type and Quantity
|
Compartment and Hanging Attachment Design
|
Material Durability
|
Special Requirements
|
|
Electrician
|
Screwdriver, voltage tester, wire stripper, measuring tape, multimeter
|
Small pocket for precision tools, large pocket for spare wires; multiple hanging loops for hanging voltage testers and measuring tapes
|
Lightweight, wear-resistant nylon, anti-static treatment
|
Electrically insulating material protection, lightweight for work at heights
|
|
Carpenter
|
Saw, hammer, plane, pencil, measuring tape
|
Large pocket for saw and hammer, small pocket for screws/pencils
|
Thickened canvas or Oxford cloth, wear-resistant and scratch-resistant
|
Nail/saw blade divider for protection against scratches
|
|
Plumber
|
Wrench, pipe wrench, scissors, tape
|
Large pocket for pliers/wrench, loop hook for measuring tape or pipe cutters
|
Oil and water resistant coating, abrasion-resistant reinforced bottom
|
Waterproof design for work in damp environments
|
|
Construction Workers
|
Hammer drill, nail gun, screws, measuring tape
|
Large pocket for heavy tools, loop hook for hammer and measuring tape
|
High-strength canvas or Oxford cloth, metal reinforced fasteners
|
High abrasion and tear resistance, lumbar decompression design for high safety
|
Design Differentiation Principles
- Capacity and Weight: High-load occupations (construction, carpentry) require larger capacity and reinforced design; electricians prioritize portability and flexibility.
- Detailed Zoning: Precision tool occupations (electricians, plumbers) prioritize smaller pockets and flexible fastening; carpenters and construction workers prioritize larger pockets and heavy-duty loop hooks.
- Materials and Protection: Damp or chemical environments require water- and oil-resistant materials; high-abrasion occupations require tear-resistant reinforcement.
- Ergonomics: Different occupational movement patterns (bending over, climbing ladders, working at heights) affect the design of the waist pack's belt, back support, and weight distribution.


 English
English  español
español