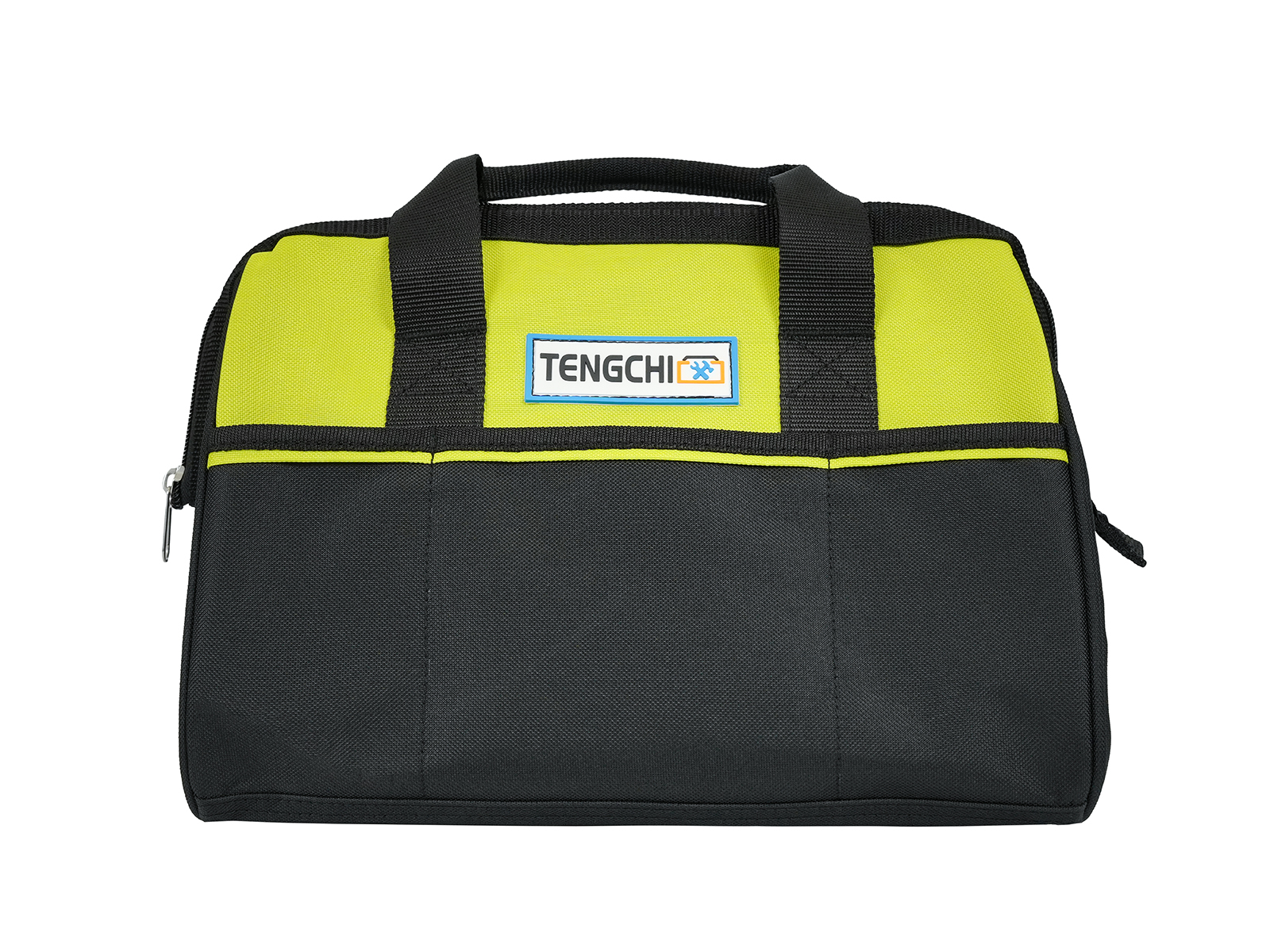
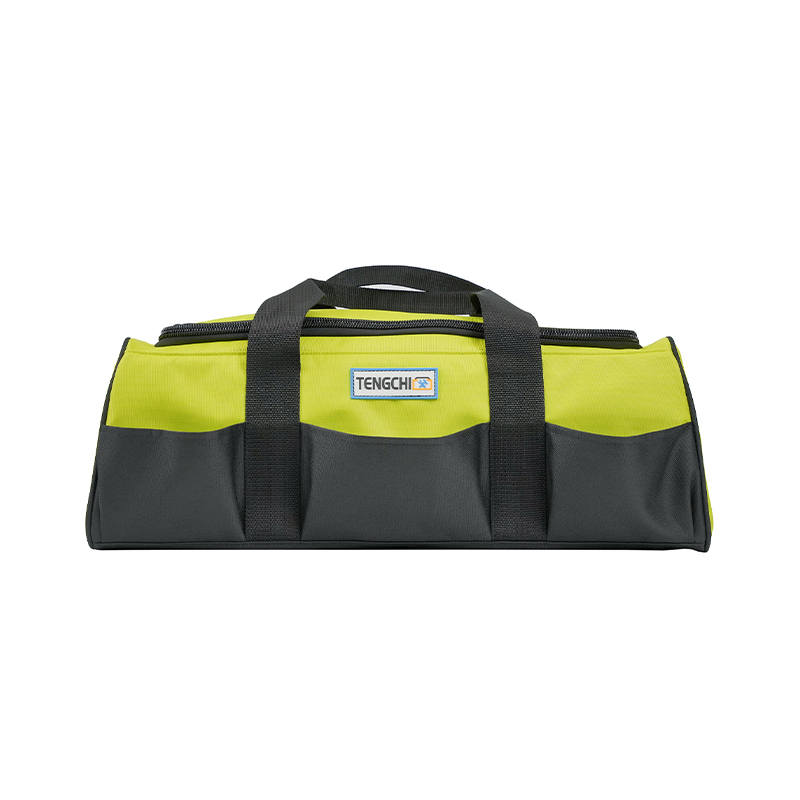
Rolling Tool Bag vs Trolley Tool Bag: Which Is Right for You?
Rolling Tool Bag Design: Key Differences Compared to Trolley Tool Bags
Structural Framework and Construction Approach
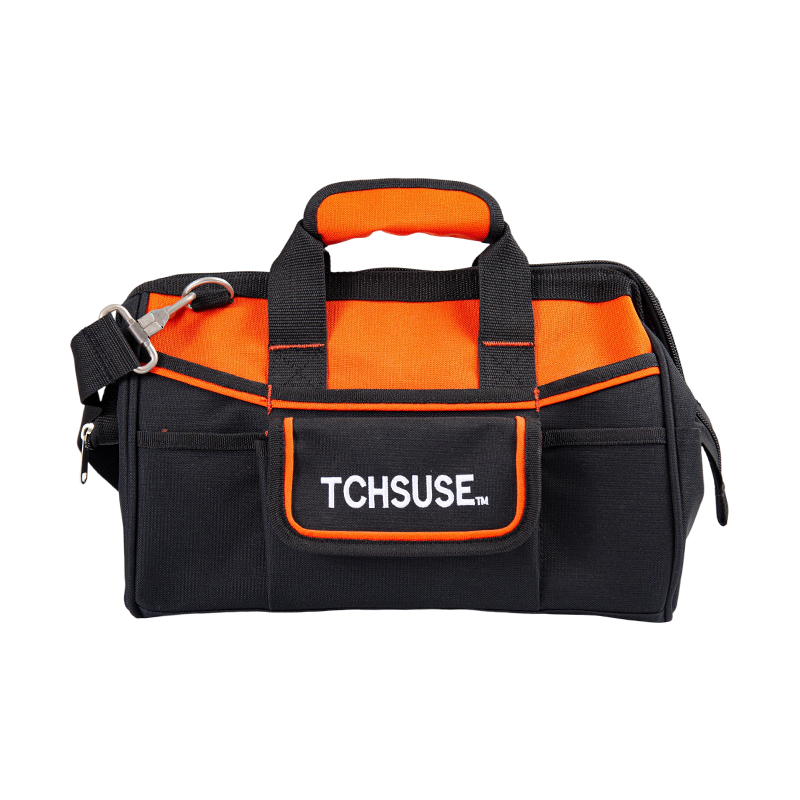
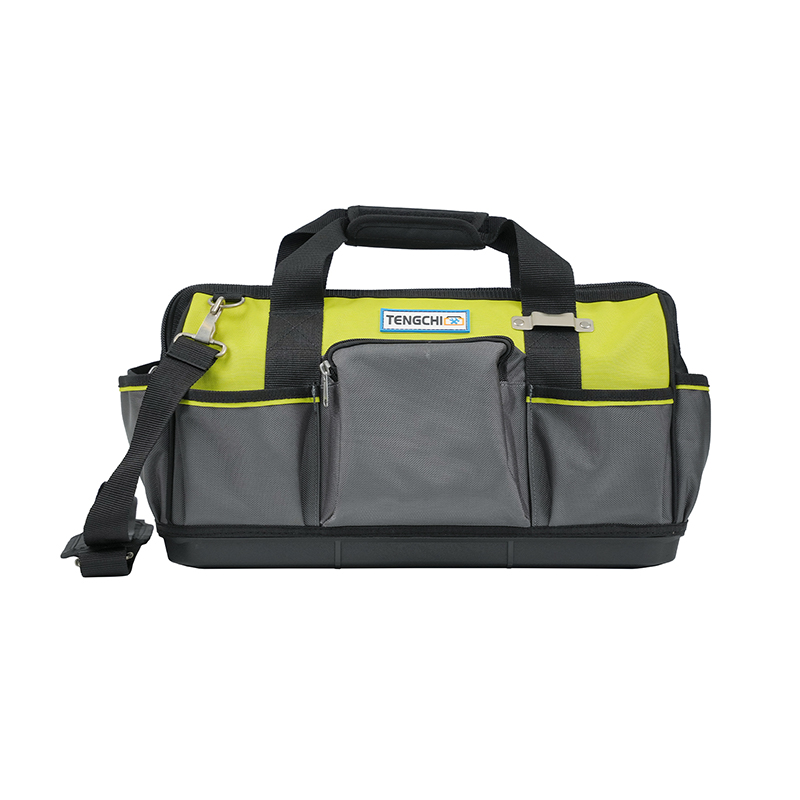
The Rolling Tool Bag is engineered with a distinctive structural framework that focuses on mobility without compromising load-bearing strength. The frame of a Rolling Tool Bag typically incorporates lightweight yet high-tensile materials such as reinforced aluminum alloy or industrial-grade plastic composite to ensure rigidity while maintaining manageable weight for transportation. The body panels are often made of abrasion-resistant 1680D ballistic polyester or heavy-duty oxford fabric layered with PVC or TPU coatings to provide exceptional resistance to tearing, water, and oil penetration. In contrast, a Trolley Tool Bag generally adopts a box-like configuration, integrating a hard shell or semi-rigid enclosure supported by a full metal frame. This gives it a higher degree of impact resistance but limits flexibility and slightly increases the overall weight, making it more suitable for stationary or site-specific applications.
Rolling Tool Bags often include flexible side panels and reinforced seams to accommodate variable tool loads. Stitching techniques such as triple-lock or bar-tack reinforcement are applied to handle joints, wheel mounts, and shoulder strap anchors. The handles are commonly riveted into reinforced metal plates that distribute stress evenly during movement, whereas Trolley Tool Bags employ bolted handle mechanisms connected to the rigid frame. The design difference is evident when the bags are subjected to continuous mobility across uneven terrain—Rolling Tool Bags absorb vibration through their fabric elasticity, while Trolley Tool Bags rely on mechanical rigidity for stability.
Wheel Mechanism and Mobility System
The wheel system of a Rolling Tool Bag represents one of its most defining design elements. Premium designs use oversized rubberized or polyurethane-coated wheels mounted on steel bearings to ensure smooth rolling over concrete, gravel, or industrial floors. Dual-wheel or tri-wheel assemblies are implemented to enhance stability and reduce resistance during incline navigation. Many Rolling Tool Bags use a recessed wheel design to protect the wheels from external impact, allowing them to maintain functionality in rugged environments.
By comparison, Trolley Tool Bags feature larger, exposed wheels similar to those used in luggage trolleys, offering efficient straight-line motion but less adaptability on uneven surfaces. The wheel mounts in a Trolley Tool Bag are fixed to a rigid frame extension, while Rolling Tool Bags typically integrate a shock-absorbent wheel housing that minimizes vibration transfer to the tools inside. This design detail prevents tool disorganization and protects sensitive instruments such as electrical testers or calibration devices from micro-impacts during transit.
Handle Engineering and Ergonomic Considerations
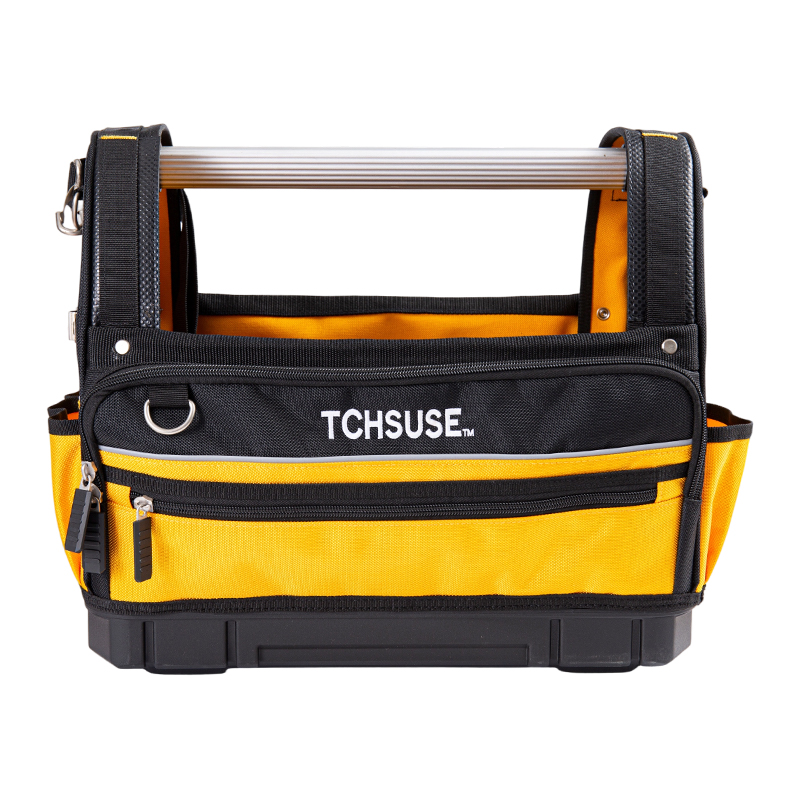
A Rolling Tool Bag generally features an adjustable telescopic handle constructed from anodized aluminum tubing with multi-stage locking positions, allowing customization according to user height. The ergonomic focus extends to the handle grip, which is molded from thermoplastic rubber or EVA foam to provide comfort during prolonged use. Some advanced Rolling Tool Bag models employ dual-handle systems—a retractable trolley handle for rolling and padded carry handles for manual lifting.
In contrast, Trolley Tool Bags are primarily designed with a fixed or semi-retractable handle mechanism that integrates directly into the hard frame. Although sturdy, these handles are less flexible in adjustment range and often heavier due to their steel composition. The ergonomic advantage of the Rolling Tool Bag lies in its dynamic adaptability to user posture, reducing wrist strain and optimizing push-pull balance during movement. This makes Rolling Tool Bags especially suitable for technicians who frequently move between job sites, while Trolley Tool Bags serve better in environments where the bag remains mostly stationary or transported occasionally over short distances.
Internal Compartment Design and Tool Arrangement Logic
The interior configuration of a Rolling Tool Bag is optimized for modular organization. Designers prioritize accessibility and visibility of tools without requiring users to unload the entire contents. Multi-layer compartments, detachable tool panels, and elastic retention loops allow customized tool positioning. Some Rolling Tool Bags incorporate vertical storage systems, enabling users to access tools while the bag stands upright. This prevents spillage and maximizes working efficiency on-site.
Trolley Tool Bags, however, typically provide deeper, box-like storage compartments, offering higher capacity for bulky tools but lower accessibility for small items. Their compartmentalization relies on rigid dividers or molded trays rather than flexible pouches. The Rolling Tool Bag’s design advantage lies in its adaptability—it accommodates both hand tools and electronic equipment by balancing protection padding with flexibility. Advanced models from companies like Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. integrate removable tool boards and Velcro-adjustable sections, allowing technicians to reconfigure the layout based on their workflow requirements.
Base Reinforcement and Load Distribution
The base of a Rolling Tool Bag is strategically engineered to distribute weight evenly across the wheel axis, preventing sagging and ensuring stability during rolling. Reinforced with molded HDPE (high-density polyethylene) or aluminum plating, the base resists deformation under heavy loads. Drain holes are sometimes added to prevent liquid accumulation during outdoor operations.
A Trolley Tool Bag, being more rigid, uses a solid integrated chassis that supports vertical loading more effectively but may lack flexibility when navigating over irregular surfaces. While both designs aim for structural integrity, the Rolling Tool Bag incorporates shock-absorbing pads or rubber feet at contact points to minimize surface abrasion and extend material longevity. This feature proves particularly useful for field technicians working in diverse conditions such as workshops, construction sites, or maintenance zones.
Weight Management and Portability
Portability defines the core design principle of a Rolling Tool Bag. By distributing tool weight over the wheel axis, it allows users to transport heavy loads with reduced physical effort. The average Rolling Tool Bag weighs between 6–10 kg when empty, offering a favorable balance between strength and maneuverability. Manufacturers optimize the frame-to-body ratio to maintain low center of gravity for improved rolling stability.
In contrast, a Trolley Tool Bag—due to its heavier frame and rigid shell—can weigh up to 15 kg or more, prioritizing protection over mobility. Although its sturdiness provides superior impact resistance, the design is less efficient for frequent movement. For professionals who need to carry the bag up stairs or load it into vehicles, the Rolling Tool Bag presents a clear ergonomic advantage through its hybrid portability—users can both roll and carry it comfortably when needed.
Material Innovation and Longevity
Modern Rolling Tool Bags integrate advanced synthetic textiles like Cordura nylon, ballistic polyester, and thermoplastic elastomers. These materials are chosen for their balance between tensile strength and flexibility. Additional waterproof coatings and UV-resistant layers ensure performance stability in outdoor applications. Reinforced stitching and corrosion-resistant metal components, such as YKK zippers and stainless-steel rivets, enhance service life.
Trolley Tool Bags generally employ thicker outer shells with ABS or polypropylene reinforcements. While this structure provides superior impact absorption, it reduces flexibility under load stress. The Rolling Tool Bag’s use of textile composites allows for self-healing behavior under tension, extending the usable lifespan of fabric panels without significant weight penalty.
Functional Versatility and User Adaptation
The Rolling Tool Bag is designed to serve multiple professions, from electricians and HVAC specialists to field engineers and mechanics. Its structure accommodates a broad spectrum of tools, accessories, and digital devices. Integrated laptop sleeves, power tool pockets, and external attachment loops expand versatility. Some models from Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. even include detachable backpacks or waist pouches for added convenience.
Trolley Tool Bags, on the other hand, are often optimized for workshop or construction site use where high capacity and vertical storage are priorities. The Rolling Tool Bag’s hybrid functionality offers a more balanced approach, allowing smooth transition between indoor and outdoor environments.
Protective Design and Safety Integration
Safety in tool transportation is directly linked to the design of closure systems and internal padding. Rolling Tool Bags frequently incorporate padded compartments with EVA or PE foam linings to protect delicate instruments. Heavy-duty zippers with lockable sliders ensure security during travel. Reflective strips and reinforced corner guards enhance visibility and durability.
Trolley Tool Bags, with their rigid structure, rely on mechanical locks and hard covers for protection. However, the Rolling Tool Bag’s flexible shell absorbs external shocks more effectively during accidental drops. The integration of internal padding reduces impact transmission, maintaining tool calibration accuracy and reducing the likelihood of tool damage.
Design Philosophy and User Experience Integration
The Rolling Tool Bag is fundamentally guided by a design philosophy that merges ergonomics, modularity, and mobility. Every structural element—from the retractable handle and wheel assembly to the compartment layout—is engineered around user experience and workflow optimization. The seamless combination of soft-sided flexibility with rigid structural reinforcement distinguishes Rolling Tool Bags from Trolley Tool Bags. While the latter prioritizes static organization and heavy-duty protection, the Rolling Tool Bag embodies the modern technician’s need for efficient mobility, modular functionality, and ergonomic handling.
Rolling Tool Bag Materials and Durability for Heavy-Duty Use
High-Performance Fabric Selection and Reinforcement Technology
The foundation of a Rolling Tool Bag’s durability begins with the fabric composition. Heavy-duty applications demand materials capable of withstanding abrasion, tearing, and continuous flexing under load. The most commonly adopted fabrics are 1680D ballistic polyester, Cordura nylon, and industrial-grade Oxford fabric. Each material is engineered to provide tensile strength, puncture resistance, and longevity under extreme conditions. The 1680D polyester features double-weave construction, delivering exceptional structural integrity while maintaining flexibility for folding and mobility. In many Rolling Tool Bag designs, manufacturers apply polyurethane (PU) or thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) coatings to the inner surface of the fabric, forming a waterproof barrier that also resists oil, grease, and solvents encountered in industrial environments.
To enhance performance, additional reinforcement layers are strategically integrated at stress points such as the wheel housings, handle attachments, and corner edges. These reinforcements use dense woven nylon or rubber-backed patches, often stitched in multi-directional bar-tack patterns. Certain premium Rolling Tool Bags from Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. incorporate Kevlar fiber panels in high-stress areas, offering resistance to cutting and tearing when exposed to sharp-edged tools. The combination of flexible yet durable textile layering allows the bag to withstand repetitive folding, loading, and compression cycles without structural fatigue or seam separation, ensuring sustained functionality in long-term industrial use.
Waterproofing, Chemical Resistance, and Environmental Shielding
A critical design consideration for any Rolling Tool Bag intended for heavy-duty work is its ability to resist environmental exposure. Technicians frequently operate in wet, dusty, or chemically active locations, necessitating comprehensive protection against external contaminants. Advanced waterproofing is achieved by bonding hydrophobic coatings directly to the fabric surface during production, rather than applying post-process sprays that degrade over time. TPU and PVC coatings create a continuous impermeable layer capable of repelling water under high pressure. In field testing, these coatings are often evaluated under hydrostatic head standards exceeding 1000 mm to ensure sustained resistance during rain or fluid exposure.
Chemical resistance is equally important. Many industrial service sites involve lubricants, degreasers, and cleaning chemicals that can deteriorate fabric integrity. For this reason, Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. employs polymer coatings with added stabilizers that resist acidic and alkaline substances. The zippers, buckles, and fasteners are made from corrosion-resistant alloys or industrial-grade ABS to prevent rust and embrittlement. Dust ingress protection is achieved through tight seam sealing and zipper flaps, ensuring the Rolling Tool Bag maintains internal cleanliness for sensitive equipment such as meters, gauges, or calibration tools.
Internal Padding and Impact Protection Systems
Durability is not only determined by external toughness but also by internal protection engineering. Rolling Tool Bags designed for heavy-duty environments incorporate EVA (Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate) or closed-cell polyethylene foam padding between fabric layers to absorb vibration and impact energy. This multi-layer cushioning prevents mechanical shock from damaging tools when the bag is rolled across uneven terrain or during accidental drops. The foam density varies depending on the compartment purpose—denser foam for power tool pockets and lighter foam for flexible hand tool pouches.
Additionally, rigid panel inserts made of HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) are positioned within the bag walls and base to maintain shape and distribute stress evenly. These panels protect against deformation when the bag is fully loaded, while also improving stability during upright positioning. Internal dividers with shock-absorbent edges prevent tool collision inside compartments. Premium Rolling Tool Bags may feature floating suspension compartments, allowing delicate instruments to remain insulated from wheel vibration through suspended fabric supports. This advanced construction differentiates Rolling Tool Bags from traditional rigid trolley models that lack vibration isolation mechanisms.
Metal Component Quality and Corrosion Resistance
Heavy-duty use exposes all hardware elements—zippers, rivets, buckles, and wheel axles—to continuous friction, moisture, and physical stress. The metal components of a Rolling Tool Bag therefore require corrosion resistance and mechanical endurance equal to that of the fabric. High-end designs utilize YKK zippers fabricated from nickel-plated brass or stainless steel, chosen for their superior tensile strength and smooth sliding characteristics under tension. Pull tabs are often enlarged and rubberized for use with gloves, reflecting a design emphasis on field practicality.
Rivets and D-rings undergo zinc or chrome electroplating to resist rust in humid environments. In marine or offshore applications, manufacturers prefer marine-grade 316 stainless steel fasteners due to its molybdenum-enriched alloy composition that resists salt corrosion. The telescopic handle mechanisms employ anodized aluminum tubing to prevent oxidation, while the wheel axles are protected by sealed ball bearings with synthetic grease lubrication to minimize wear. Every component of a heavy-duty Rolling Tool Bag must maintain structural coherence despite constant exposure to vibration, humidity, and temperature fluctuations.
Wheel Assembly Durability and Terrain Adaptation
The wheel assembly is a primary determinant of a Rolling Tool Bag’s service life. Wheels endure repetitive impact and weight-bearing stress across diverse surfaces such as concrete, gravel, or asphalt. To guarantee reliability, top-tier Rolling Tool Bags employ molded polyurethane (PU) wheels that combine elasticity with abrasion resistance. PU material offers superior resilience compared to hard plastic, absorbing surface vibration and preventing flat-spot formation. The wheel cores are reinforced with glass-fiber composite hubs or aluminum centers to prevent cracking under load.
For demanding industrial environments, dual-wheel assemblies or oversized wheels are preferred, as they distribute weight more evenly and improve stability when the bag is pulled at an angle. Each wheel is mounted using a stainless-steel bearing system sealed with rubber gaskets to exclude dust and moisture. Unlike smaller trolley-type wheels, Rolling Tool Bag wheels are recessed into the base frame, reducing the likelihood of damage from lateral impacts. Some designs include replaceable wheel cartridges, enabling maintenance without disassembling the entire bag. Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. engineers its wheel housings with reinforced ABS guards that absorb external shocks and reduce structural strain on the main frame.
Base Plate Engineering and Load Support Optimization
The base plate of a Rolling Tool Bag functions as the central structural support for all load-bearing activities. Constructed from HDPE, ABS polymer, or lightweight aluminum alloy, the base ensures stability during motion and resting periods. Heavy-duty designs often include ribbed reinforcement patterns molded into the plate to enhance rigidity without adding excessive weight. The perimeter edges are sealed with rubber or silicone guards to prevent abrasion when dragging the bag across rough surfaces.
Load testing during product development verifies that the base can withstand static weights exceeding 50 kilograms without deformation. The junction between the base and fabric shell is reinforced using industrial-grade rivets and adhesive bonding for redundancy. Non-slip rubber feet are positioned at contact points to prevent sliding and elevate the bag above wet ground. Drainage channels are incorporated into certain designs to allow water to escape, preserving the internal environment. The optimized load distribution through the base reduces pressure points on wheels and handles, significantly extending the Rolling Tool Bag’s operational life compared to rigid trolley alternatives.
Seam Engineering and Stitching Reinforcement Techniques
In textile-based tool storage, seam integrity directly affects durability. A Rolling Tool Bag experiences multidirectional stress as tools shift during movement, so the stitching must withstand dynamic loads. Manufacturers use nylon or polyester bonded threads treated with anti-fray coatings. These threads maintain tensile strength even after prolonged UV and chemical exposure. The seams are commonly double-stitched with lockstitch patterns that prevent unraveling when a single thread is compromised.
Critical stress points, such as handle mounts and shoulder strap attachments, employ box-and-cross (X-box) stitching reinforced with bar-tack ends. This pattern disperses stress across multiple thread intersections rather than concentrating it at a single point. Seam taping and binding are used internally to prevent moisture ingress and protect against fraying edges. Some high-performance models feature ultrasonic welded seams, merging fabric layers without puncture holes, thus enhancing waterproofing and structural strength simultaneously. Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. integrates these sewing technologies through automated precision equipment to maintain uniform quality control in large-scale production.
Thermal and UV Stability of Outer Materials
Durability is not limited to mechanical resistance; exposure to temperature variations and ultraviolet radiation can degrade fabric and coating materials over time. Rolling Tool Bags intended for outdoor or high-heat environments use UV-stabilized coatings and pigments to prevent color fading and polymer breakdown. TPU coatings are particularly valued for their thermal elasticity—they retain flexibility at sub-zero temperatures and resist melting deformation at elevated heat levels.
For technicians working in environments such as oilfields or shipyards, heat reflection surfaces are applied using aluminum-laminate layers on exposed areas of the Rolling Tool Bag. This protects both the exterior fabric and internal contents from temperature buildup. Materials are selected based on their thermal cycling endurance, meaning the ability to expand and contract repeatedly without microcracking or delamination. Such characteristics ensure consistent performance across a wide temperature range from -20°C to +70°C.
Rolling Tool Bag Storage Capacity: Organizing Your Tools Efficiently
Internal Volume Optimization and Spatial Architecture Design
The internal architecture of a Rolling Tool Bag is engineered to achieve the optimal balance between compactness and storage efficiency. Designers focus on three-dimensional volume utilization by integrating tiered compartments, expandable panels, and modular inserts. The typical storage capacity of a professional-grade Rolling Tool Bag ranges from 50 to 100 liters, allowing it to accommodate both small precision tools and large power equipment. Internal space is measured not only by gross volume but also by accessibility, ensuring every tool can be reached without excessive unloading. The bag’s body structure often incorporates flexible dividers made from reinforced nylon mesh or HDPE panels that can be adjusted or removed according to tool dimensions.
A crucial factor influencing capacity design is the internal geometry ratio between width, depth, and height. A well-designed Rolling Tool Bag maintains a low center of gravity to prevent tipping when heavily loaded. The bag base may extend slightly wider than the top section to distribute weight evenly over the wheel axis. In products engineered by Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd., CAD-assisted spatial modeling is applied during the design phase to simulate load distribution under different packing conditions. This technology allows precise allocation of internal space for distinct tool categories, improving both packing density and user convenience. The structured yet flexible compartment layout eliminates wasted volume and enhances tool accessibility during worksite operations.
Compartmentalization and Multi-Layer Layout Engineering
A Rolling Tool Bag’s effectiveness relies on its ability to separate tools systematically. The compartmentalization strategy incorporates multiple horizontal and vertical layers to maximize functional storage zones. The main compartment typically houses power tools, measuring devices, and bulkier hand instruments. Secondary compartments positioned at the front or sides are used for smaller components such as sockets, drill bits, or fasteners. The inclusion of tiered internal trays or detachable tool boards allows users to organize by tool type or job function.
In high-capacity models, an accordion-style compartment system is utilized. This design enables each layer to expand independently, providing full visibility without obstruction. Dividers reinforced with semi-rigid foam panels prevent sagging and tool shifting during transportation. Tool pouches and slots are arranged with an ergonomic focus—commonly in an angled configuration to minimize bending or searching time. Elastic retention loops made of industrial-grade rubber maintain tension over years of use. The modular compartment system in Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. Rolling Tool Bags allows users to reconfigure their internal layout by attaching or detaching pouches using Velcro or MOLLE webbing. This design principle ensures adaptable storage organization for electricians, mechanics, HVAC technicians, and construction professionals who require customized configurations for varied task sets.
Vertical Storage Systems and Upright Accessibility
Vertical organization represents one of the most significant innovations in Rolling Tool Bag design. Unlike traditional horizontal tool cases that require users to stack tools on top of each other, vertical systems allow direct visibility and single-hand access to every tool. The vertical slot design accommodates wrenches, pliers, and screwdrivers in an upright position, supported by reinforced pockets stitched to internal panels. Each slot is proportionally sized to ensure a snug fit that prevents movement during transport.
The upright design enhances workflow efficiency in field environments. Technicians can roll the bag to a work zone, open it, and immediately access tools without unpacking the entire contents. To support this function, the bag’s base structure is engineered with anti-topple reinforcements. This includes a widened stance and internal stiffeners that maintain balance when the front flap is open. For electrical or plumbing specialists, Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. integrates transparent pocket linings made of clear thermoplastic film, allowing instant visual identification of stored items. The upright system not only increases capacity utilization by reducing stacking gaps but also ensures better protection for delicate instruments by isolating them vertically from heavier equipment.
Detachable Modules and Customizable Inserts
Heavy-duty Rolling Tool Bags increasingly adopt modularity as a design standard. Detachable inserts, often in the form of removable pouches, trays, or tool boards, offer flexibility for professionals managing diverse projects. Each insert can serve as a mini toolkit, containing specific tool groups required for a given task. When not needed, these modules can be removed to reduce weight or replaced with alternative configurations.
In the Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. modular system, detachable panels are connected via high-strength hook-and-loop fasteners or quick-release buckles. The panels are fabricated from semi-rigid polymer sheets laminated with abrasion-resistant fabric to maintain dimensional stability. For small component organization, removable zippered pouches made from transparent PVC are included, allowing clear visibility of screws, bolts, and fittings. Power tool compartments feature Velcro straps and padded inserts to hold drills and impact drivers securely. This modular approach ensures optimal space management while allowing complete personalization of tool arrangement according to trade requirements. By separating compartments based on daily usage frequency, users can reduce time wasted searching for tools and maintain a consistent workflow.
Side Pockets, External Compartments, and Accessibility Engineering
The external structure of a Rolling Tool Bag plays an essential role in expanding storage capacity beyond the internal core. Designers incorporate side pockets, front compartments, and top-access flaps for quick retrieval of frequently used tools. These pockets are constructed with gusseted expansions that increase depth when filled, supported by double zippers for easy opening. External pockets are strategically positioned to maintain balance and prevent the bag from leaning under asymmetrical loads.
Certain models include hard-shell exterior compartments for delicate items such as meters or gauges. These compartments are lined with EVA foam to protect instruments from vibration. The top-access compartment often integrates a small tool tray, providing a flat workspace for screws or connectors during repair tasks. Elastic mesh pockets and D-ring attachments on the exterior allow temporary storage of gloves, tape measures, or cables. Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. ensures that each pocket’s location corresponds to ergonomic reach zones based on anthropometric studies, meaning users can access external tools without excessive bending or repositioning. The well-planned distribution of external storage zones transforms the Rolling Tool Bag into a mobile workstation capable of holding an extensive range of tools while maintaining balance and structural integrity.
Load Distribution and Weight Management Principles
Efficient tool organization depends on balanced load distribution to maintain mobility and structural longevity. In a Rolling Tool Bag, heavy tools should be positioned near the wheel axis and lower sections to reduce strain on handles and prevent tipping. Designers consider weight dynamics when defining compartment size and placement. Reinforced lower compartments are engineered to hold power tools such as drills, saws, or grinders, while upper and side pockets handle lightweight accessories.
The internal structure often includes compression straps or tie-down loops that stabilize tool weight during motion. The handle attachment area is fortified with load-bearing plates that channel force directly to the base frame instead of fabric panels. In advanced designs, dynamic load modeling is used to simulate how internal weight shifts during rolling, allowing reinforcement points to be adjusted for long-term durability. The wheel bearings and axles are also selected based on projected weight distribution, ensuring smooth movement even when the Rolling Tool Bag reaches maximum capacity. Products from Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. integrate adjustable partition systems enabling users to redistribute weight depending on the day’s tool requirements, maintaining a consistent center of gravity for optimal handling.
Integration of Specialized Tool Holders and Mounting Systems
To enhance organization efficiency, Rolling Tool Bags incorporate specialized holders and mounting systems tailored to professional tool categories. For electricians, elastic insulated slots hold screwdrivers and pliers in isolated channels. Mechanics benefit from wrench racks and socket organizers built into inner panels. HVAC technicians utilize adjustable strap systems to secure hoses and measuring devices. Each mounting accessory is constructed from elastic nylon webbing or injection-molded ABS clips capable of withstanding repeated stretching.
Innovative designs also include magnetic tool strips embedded along interior panels for holding metallic tools, preventing them from shifting during transit. Velcro-backed mounts enable users to attach custom tool pouches or instrument cases. Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. has developed a proprietary modular mounting grid compatible with standard MOLLE accessories, offering full adaptability for users who wish to attach third-party tool pouches or test equipment holders. This integration of purpose-built storage elements within the Rolling Tool Bag framework transforms it from a passive container into a dynamic, user-customizable system for tool organization and transport.
Protective Compartments for Electronic Devices and Documentation
Modern technicians often carry not only mechanical tools but also electronic devices such as tablets, laptops, and diagnostic instruments. Rolling Tool Bags designed for heavy-duty use incorporate padded compartments lined with anti-static fabric to safeguard electronics from impact and electromagnetic interference. The laptop compartment typically uses 10–15 mm EVA padding enclosed in a waterproof sleeve to resist moisture ingress. Cable organizers and charger pockets are integrated to prevent tangling and ensure quick deployment on-site.
In addition to digital devices, a documentation pocket lined with waterproof material allows safe storage of manuals, blueprints, or compliance certificates. These compartments are usually located on the bag’s upper section for rapid access without exposing the entire tool storage area. The inclusion of technology-specific storage solutions increases total functional capacity without compromising mechanical tool organization. Yancheng Tengchi Tourism Products Co., Ltd. designs these pockets with heat-reflective materials to maintain safe operating temperatures for electronics during outdoor operations.
Rolling Tool Bag Mobility: Wheels, Handles, and Ergonomic Advantages
Wheel Design and Construction for Smooth Mobility
The mobility of a Rolling Tool Bag primarily depends on the design and construction of its wheels. Manufacturers focus on wheel diameter, tread material, bearing quality, and mounting position to ensure smooth, stable movement across diverse surfaces. Larger wheels, typically 3 to 5 inches in diameter, allow smoother rolling over uneven ground such as gravel, workshop debris, or construction flooring. Smaller wheels, on the other hand, are suited for indoor environments where compactness and maneuverability are prioritized. Wheel treads are often made of thermoplastic rubber (TPR) or polyurethane, which provide a combination of flexibility, wear resistance, and vibration absorption. Some high-end models utilize pneumatic wheels filled with air or foam, enabling shock absorption and better adaptability to outdoor conditions.
The axle and bearing systems inside the wheel assemblies determine how effortlessly the Rolling Tool Bag glides under load. Precision-sealed ball bearings reduce friction and protect the internal structure from dust or moisture intrusion. Many industrial-grade designs feature dual-bearing wheels that maintain balance even when the bag is heavily loaded with metal tools. The wheel housing is reinforced with either steel or high-density polymer to prevent deformation caused by continuous rolling pressure. Placement of the wheels also affects stability—wide wheel spacing ensures balance, while swivel-mounted front wheels improve directional control in narrow pathways.
Noise reduction is another factor considered in modern Rolling Tool Bag design. High-friction rubber wheels can generate unwanted noise when used on hard surfaces like tiles or metal grates, so soft rubber compounds or tread pattern optimization are applied to minimize rolling noise. Manufacturers that emphasize ergonomic design also integrate shock-absorbing wheel mounts that cushion the impact when the bag transitions between surfaces or is dragged up steps. The end result is a mobility system that allows professionals to transport heavy tools with minimal strain and disturbance in any environment.
Handle Design and Height Adjustment Mechanisms
The handle system of a Rolling Tool Bag directly determines user comfort during prolonged use. Modern designs often incorporate telescopic handles constructed from lightweight aluminum alloys or stainless steel tubing. These handles can be extended or retracted smoothly using push-button locking systems, allowing adjustment to different user heights. This customization minimizes bending or shoulder lifting, reducing muscle strain during transport. The handle grip itself is engineered with ergonomic principles in mind, often featuring soft thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) or foam overlays that prevent slippage and increase comfort during long carrying sessions.
Reinforcement at the handle’s connection point is another critical factor in durability. Weak attachment joints are prone to bending or detachment under high stress, especially when the Rolling Tool Bag carries power tools or mechanical parts. To overcome this, many high-quality designs use riveted or welded joints, sometimes supplemented with internal metal plates or cross braces for stability. Some brands integrate dual-handle systems—one retractable trolley handle and one fixed carrying handle—to provide versatility when lifting the bag into vehicles or up stairs.
Innovative handle configurations also appear in professional-grade Rolling Tool Bags. Articulated handles can pivot to maintain optimal balance when rolling uphill or downhill, while side handles enable two-handed lifting. Certain models incorporate anti-vibration inserts that absorb feedback from rough surfaces, keeping hand fatigue to a minimum. When the handle system aligns with the user’s height, posture remains upright, which is an essential factor in ergonomic tool transport. A poorly aligned handle can lead to uneven weight distribution, forcing the user to exert more pulling force and increasing the risk of strain injuries. Manufacturers who prioritize ergonomics often design handles with multi-angle locking systems to provide stable control regardless of the terrain or direction of movement.
Ergonomic Weight Distribution and Stability Control
A Rolling Tool Bag’s ergonomics are not limited to its handles and wheels; the internal structure and overall balance play an equally vital role in user comfort. The placement of heavy tools within the bag must correspond to the wheel axis to prevent tipping. Many premium Rolling Tool Bags use a low-center-of-gravity design where heavy compartments are located near the wheelbase. This stabilizes the bag when navigating uneven ground or making sharp turns. The frame’s rigidity also contributes to maintaining structure under pressure. Reinforced polymer frames or internal steel rods prevent the bag from collapsing or twisting when heavily loaded.
The ergonomic advantage is further enhanced by distributing compartments evenly along the vertical axis. Top-heavy configurations cause instability, leading to wobbling during transport. To counteract this, designers add wide base platforms and anti-tip supports at the rear of the bag. Some Rolling Tool Bags include integrated stabilizer bars or kickstands that hold the bag upright when stationary. The handle alignment and wheelbase geometry are engineered to ensure that the pulling force remains aligned with the center of gravity. This alignment reduces lateral stress on the user’s wrist and shoulder joints.
Another consideration in ergonomic design is vibration transfer. When rolling over hard surfaces or gravel, vibrations can travel through the handle into the user’s hand. To address this, manufacturers apply vibration-damping materials such as silicone inserts or elastomeric mounts in both the handle and wheel assembly. These components absorb micro-shocks and prevent user fatigue. In professional use, where technicians frequently move the bag between workstations, minimizing physical fatigue directly improves efficiency and safety.
Multi-Surface Adaptability and Terrain Performance
Mobility performance is determined not just by wheel size or bearings but by the ability of the Rolling Tool Bag to adapt to different terrains. Indoor surfaces like smooth concrete, epoxy-coated floors, and tiles require wheels that provide minimal resistance and high control precision. In contrast, outdoor construction sites, warehouses, and service yards demand rugged tread patterns and materials that resist puncture and abrasion. Rolling Tool Bags built for mixed environments often use dual-wheel configurations—two large rear wheels for outdoor rolling and smaller swivel front wheels for indoor maneuvering.
The clearance height of the wheelbase also influences usability on uneven terrain. Bags with elevated wheel mounts can climb curbs or small steps more easily without dragging the frame. Some advanced models integrate retractable wheel guards or wheel arch shields to protect against mud, water, or debris ingress. These guards ensure consistent wheel rotation even when exposed to dirt or moisture. In wet environments, sealed bearings and corrosion-resistant axles prevent rusting and maintain smooth operation over time.
For professionals working in environments such as oil refineries or marine docks, anti-slip wheel compounds are preferred to ensure traction on slick floors. Heavy-duty models even feature quick-release wheel systems that allow users to replace damaged wheels without disassembling the frame. This feature is particularly valuable for technicians who rely on uninterrupted mobility in remote job sites. The capacity of a Rolling Tool Bag to handle multiple terrain conditions without manual lifting is one of the strongest ergonomic advantages over traditional tool bags.
Enhanced User Comfort Through Design Integration
The most effective Rolling Tool Bags achieve superior mobility through holistic design integration, combining wheels, handles, and frame geometry into one cohesive ergonomic system. When every structural element functions in harmony, the user experiences reduced pulling effort, smoother transitions, and better overall stability. The handle and wheel system must be calibrated to maintain linear motion with minimal resistance, ensuring that the user’s hand trajectory aligns with the motion of the wheels.
Designers often conduct biomechanical studies to identify the ideal height and angle for handle positioning. This research informs adjustments that reduce muscle strain on the forearm and shoulder. The bag’s frame geometry complements this by aligning the load path directly over the wheelbase, minimizing torque and preventing twisting during turns. A high-quality Rolling Tool Bag includes padding on critical touchpoints such as handle grips, side panels, and lifting zones to prevent discomfort during frequent repositioning.
Manufacturers are increasingly implementing data-driven improvements, using motion analysis and user testing to refine ergonomics. For example, a prototype Rolling Tool Bag may undergo simulations that measure hand force, wrist angle, and step frequency over various surfaces. The resulting data helps engineers redesign handle curvature, wheel size, or center-of-gravity alignment to achieve maximum comfort and efficiency. This process produces Rolling Tool Bags that not only move smoothly but also protect the user from repetitive stress injuries commonly associated with heavy tool transportation.
Integration of Suspension and Shock-Absorption Technologies
Some premium Rolling Tool Bags now include integrated suspension systems similar to those used in travel luggage or industrial carts. These systems employ spring-loaded or elastomeric mounts that isolate the main body from wheel impact. This design minimizes vibrations transmitted to the tools inside, reducing wear and tear on sensitive equipment such as precision instruments or electronic meters. Suspension-enhanced Rolling Tool Bags also enhance user comfort by dampening abrupt movements when transitioning between surfaces or descending small steps.
Shock-absorbing technology can also be implemented within the wheel composition itself. Multi-layer wheel structures combine rigid inner cores with flexible outer treads that compress slightly upon contact with the ground, dispersing kinetic energy. Handles may incorporate dampening rods or cushioned sleeves to further soften the pull. In heavy-duty applications, these mechanisms prevent jarring motions that could destabilize the load or strain the user’s arm. By reducing mechanical vibrations and sudden jolts, suspension-enhanced Rolling Tool Bags provide a superior experience in both industrial and mobile fieldwork environments.


 English
English  español
español